A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Galvanized Coil Slitting Lines
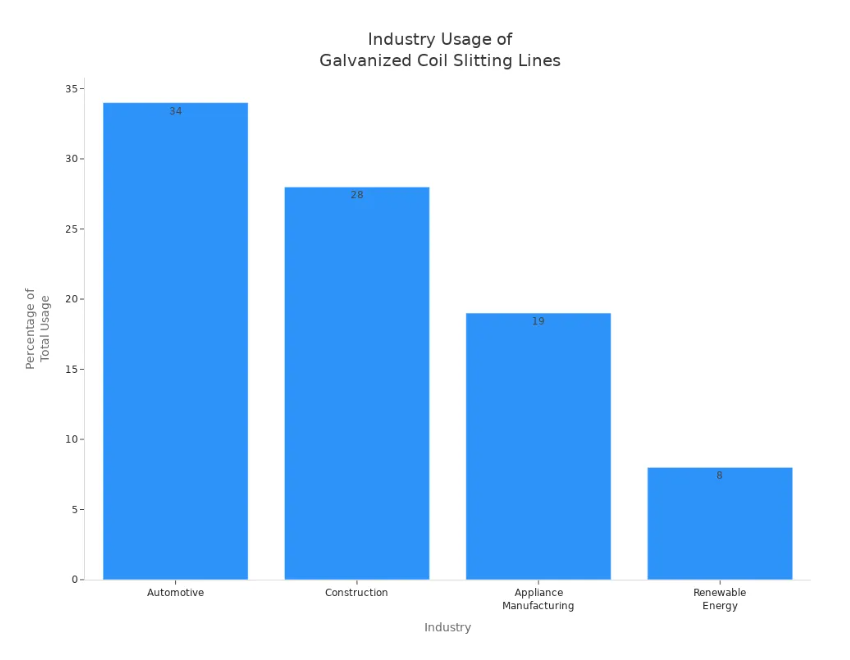
A galvanized coil slitting line cuts big galvanized steel coils. It makes them into smaller strips. Many industries use these strips. These lines are very important in cars, building, making appliances, and clean energy. The car industry uses the most, with 34%. Construction and appliances come next. The chart below shows how each industry uses these lines:
|
Industry |
Percentage of Total Usage |
Key Applications and Notes |
|
Automotive |
34% |
This is the biggest user. They use slit coils for car parts like door beams, seat frames, and chassis. Electric cars need more too. |
|
Construction |
28% |
They use slit coils for roofing, wall covers, and building parts. Big building projects around the world increase this need. |
|
Appliance Manufacturing |
19% |
They use slit coils in fridges, ovens, and washing machines. People want special finishes and rust protection. |
|
Renewable Energy |
8% |
This is a new area. Slit coils are used in solar panel mounts and wind turbines. |
|
Packaging |
Smaller share |
They use thin slit coils for food cans and spray containers. |
Key Takeaways
· Galvanized coil slitting lines cut big steel coils into smaller strips. These strips are used in cars, buildings, and home appliances. These machines use automation and careful controls to make good strips fast. This saves time and cuts down on waste. Keeping the right tension and checking quality stops damage. It also makes sure strips are smooth and correct for better products. Picking the best slitting line depends on coil size and material. It also depends on how much you need to make and what automation you want. This helps your business reach its goals. Doing regular maintenance and following safety rules keeps the slitting line working well. It also keeps workers safe and helps things run better.
What Is a Galvanized Coil Slitting Line
Purpose and Use
A galvanized coil slitting line helps cut big metal coils into smaller strips. First, you put a master coil on the machine. The line unwinds the metal and flattens it. Then, rotary knives cut the metal into thin strips. Each strip is the right width for your next job. The machine rolls up these strips into smaller coils. You can use these coils for rolling, welding, bending, or punching.
A galvanized coil slitting line works with many metals. It can handle galvanized steel, cold rolled steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. The table below lists some common materials:
|
Material Category |
Examples Included |
|
Steel Coils |
Galvanized plate, cold rolled sheet, color coated sheet, pickled plate |
|
Non-ferrous Metals |
Tinplate, copper plate, aluminum strip |
|
Specialty Steel Sheets |
Silicon steel sheet, stainless steel sheet |
This machine uses high automation. It has PLC and HMI controls. These controls make it easy to use and fast. You can change the blade settings for different sizes and metals. The system also keeps the right tension and collects scrap. This gives you clean and accurate strips every time.
Tip: A galvanized coil slitting line saves time and work. You can finish more coils faster and make fewer mistakes.
Importance in Industry
You will see galvanized coil slitting lines in many places. They are important in cars, building, electrical, and packaging. For example, slit coils help make car doors, roofing, transformer cores, and food cans. Here are some common uses:
- Construction: roofing sheets, wall panels, ceiling tiles
- Automotive: door frames, seat brackets, fenders
- Electrical: transformer cores, motor laminations
- Packaging: metal cans and containers
- Other uses: animal tags, brush making, roll-forming, springs, HVAC parts, appliance parts
A galvanized coil slitting line makes your work faster. The line can run without stopping a lot. You can change blades quickly and use automatic controls to switch jobs fast. The table below shows how these features help your work:
|
Feature Category |
Description |
Impact on Production Efficiency |
|
Continuous Processing |
The slitting line runs without stopping often. |
This helps you get more work done with less waiting. |
|
Quick Blade Change |
You can change blades fast with special systems. |
This means you can start new jobs sooner. |
|
High Automation |
The line controls tension, speed, and centering by itself. |
This makes it easy to use and needs less work from people. |
|
High Precision |
The blades can be set very carefully. |
This gives you smooth edges and less waste. |
|
Uniform Tension Control |
The line keeps the same pull on the metal. |
This stops the metal from wrinkling or bending. |
|
Material Adaptability |
You can change blade settings for different metals and thicknesses. |
This lets you work with many kinds of metal. |
|
Cost-Effectiveness |
The line uses most of the metal and needs little fixing. |
This saves money and cuts down on waste. |
|
Intelligent Control Systems |
The line has PLC and HMI screens with alarms. |
This keeps things safe and lets you change settings fast. |
|
Environmental Friendliness |
The line collects scrap and saves energy. |
This helps the environment and uses less power. |
You also get better products for your customers. New slitting lines can cut very close to the right size, within ±0.1 mm. Automation and real-time checks help stop mistakes and save material. The chart below shows how automation lowers labor costs and mistakes:

When you use a galvanized coil slitting line, you get better products, more output, and lower costs. You also help make work safer and greener.
Process Overview
Step-by-Step Workflow
A galvanized coil slitting line transforms large galvanized steel coils into precise, narrow strips. You can follow these steps to understand how the process works from start to finish:
- Load the Coil: Place the galvanized coil onto the coil car. The car moves the coil into position for the next step.
- Uncoil and Flatten: The hydraulic decoiler holds the coil and unwinds it. The pinch roll flattens the coil head and feeds it forward.
- Prepare the Strip: The strip passes through a leveling section. This step ensures the metal is flat and ready for slitting.
- Trim the Edges: A trimming shear removes any rough or uneven edges from the leading end of the strip.
- Guide to Slitter: The lifting roller table guides the strip to the slitting blades.
- Slit the Coil: The main slitter uses rotary knives to cut the coil into strips of the required width.
- Collect Scrap: The scrap winder gathers the trimmed edges and scrap material.
- Tension and Separation: The slit strips pass through a separator and tension station. This keeps each strip straight and prevents tangling.
- Recoil the Strips: The recoiler winds each strip into a new, smaller coil. The support arm helps keep the coils aligned.
- Inspect and Bundle: Operators check the width and thickness of each strip. They bundle and unload the finished coils for packaging and shipping.
Note: Modern slitting lines use hydraulic, pneumatic, and electronic controls. These systems help you achieve high precision and efficiency at every step.
You can see how different slitting lines compare in speed and capacity. The table below shows typical line speeds and thickness capabilities:
|
Parameter |
AlphaCo HG-25 |
BetaCut ProSeries |
GammaSlit Ultra |
|
Max Thickness |
22 mm |
25 mm |
20 mm |
|
Line Speed |
400 m/min |
350 m/min |
420 m/min |
Some heavy-duty lines can process up to 120 metric tons per hour. Industry leaders offer maximum speeds up to 800 meters per minute, much higher than the industry average of 600 meters per minute.

Quality and Tension Control
You must pay close attention to quality and tension control during slitting. These factors protect the galvanized coating and ensure each strip meets your standards.
- Operators set the slitting knives with great care. You must match the knife position to the desired strip width, material thickness, and knife diameter.
- Proper tension settings on both the uncoiler and recoiler are critical. If you set the tension too high, the steel may stretch or break. If you set it too low, the coil may telescope or collapse, causing jams and scrap.
- Tension stands help keep the coil tight. You can use pad, roll-pad, bridle roll, or roll tension stands. Roll tension stands work well for galvanized steel because they move with the strip and reduce surface damage.
- The material of the tension rolls matters. Nonwoven synthetic covers grip the strip and prevent scratches. Polyurethane rolls suit clean, dry materials but may cause damage if debris sticks.
- Hold-down rolls, also called snubber rolls, keep the outer coil lap tight. This prevents the coil from loosening and scratching the inner wraps.
- Precision-ground recoiler drums help you avoid reel marks and keep the coil surface smooth.
- Overarm supports must be balanced and aligned. Poor alignment can cause grooves or marks on the coil.
Tip: Always check the coil sidewall for movement. A marked line helps you spot improper tension right away.
If you do not control tension properly, you may face several problems:
- The coil can stretch, break, or develop wavy edges.
- You may see edge damage, bending, or crimping.
- Low tension can cause vibration marks and surface defects.
- These issues increase scrap, slow down production, and create safety hazards.
To maintain high quality, you should:
- Feed the strip straight and evenly into the knives.
- Inspect the slit width and thickness regularly.
- Monitor the process for burrs or edge waviness.
- Perform regular maintenance and sharpening of the knives.
- Use edge conditioning after slitting to remove burrs and smooth the edges. This step improves safety and gives your product a clean, uniform look.
A galvanized coil slitting line with proper tension and quality control delivers precise, high-quality strips. You can meet customer requirements and reduce waste by following these best practices.
Key Components
A galvanized coil slitting line has many main parts. Each part helps turn big steel coils into smaller strips. You need to know these parts to see how the system works.
Uncoiler (Decoiler)
The uncoiler holds and unwinds the heavy steel coil. You load the coil with a crane or forklift. The uncoiler grips the coil so it does not slip. It feeds the metal strip into the line. You can change the speed and tension to match the rest of the system. Safety features like brakes and guards keep you safe while working.
|
Aspect |
Description |
|
Uncoiler unwinds big metal coils and feeds the strip into the slitting line. |
|
|
Tension Control |
Keeps the right tension so the metal feeds evenly. This stops bending or breaking. |
|
Speed Synchronization |
Makes sure the uncoiler and slitting machine move at the same speed. This stops jams. |
|
Safety Features |
Has brakes, safety chucks, guards, and sensors to stop accidents while unwinding. |
Tip: Always check if the coil is tight before you start.
Slitting Section
The slitting section uses rotary knives to cut the metal strip. You can move the knives to make different widths. Modern machines use strong blades for sharp cuts. Automation and real-time checks help you cut the right size and waste less.
Recoiler
The recoiler rolls up the slit strips into new coils. You need the recoiler to keep the right tension. This stops loose wraps and edge damage. Separator disks keep each strip in place. Tension stands and looping pits help with different strip sizes. Good tension means you get smooth coils ready to ship or use.
- Keeps tension even for good coils
- Stops strip damage and edge problems
- Makes tight, straight coil sides for easy moving
Entry Coil Car
The entry coil car moves the heavy coil into place for loading. You use this car to save time and avoid lifting by hand. It helps line up the coil, making the start safer and faster.
Support Equipment
Support equipment includes many helpful tools. You might use air knife systems to control zinc coating. Position control systems help you make small changes. Stabilization systems stop vibration. Hydraulic expansion slitters let you change blades quickly. Coil levelers and tension leveling tools make the metal flat and less stressed. Oscillating and rotary shears cut coils into blanks fast and accurately. Multi-blanking lines can slit and cut to length for more options.
Note: Each support tool helps you work faster, make better coils, and keep your slitting line running well.
Types and Applications
Line Variations
There are different types of galvanized coil slitting lines. Each type is made for certain metal thicknesses and properties. Manufacturers build these lines with special parts. Some parts are hydraulic loading coil cars and double support uncoilers. Others are leveling machines, trimming shears, and smart control systems. These features help you work with many coil sizes and materials.
The main types are based on how thick the coil is. You can look at the table below to see the most common types:
|
Type |
Coil Thickness Range |
Description |
|
Light Gauge Steel Slitting Line |
Works with thin, light metal coils. Gives high accuracy and stops bending. |
|
|
Medium Gauge Steel Slitting Line |
3.0–6.0 mm |
Cuts thicker coils. Gives strong cutting and good results for medium thickness. |
Some slitting lines are custom-made. These lines fit your needs for material, size, and speed. The blade strength and machine setup change for each metal. This lets you use galvanized steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and more.
Tip: Pick a slitting line that matches your coil thickness and how much you want to make. This helps you get the best results and saves money.
Industry Uses
Many industries use galvanized coil slitting lines. Each industry likes galvanized steel because it does not rust and is strong. Here are some common ways people use these lines:
- Automotive: Slit galvanized steel is used for car bodies, door beams, and chassis. Suppliers say they work faster and waste less when using custom slitting lines for strong steel.
- Construction: Builders use slit coils for steel frames, balconies, fences, roofs, and HVAC ductwork. Galvanized steel is great for outdoor and building parts because it does not rust.
- Energy: Wind and solar projects use hot-dipped galvanized steel for mounts and frames. These parts must last in bad weather.
- Agriculture: Farmers use galvanized steel for equipment that does not rust and lasts longer.
- Telecommunications: Companies use galvanized steel for wiring, equipment boxes, and towers. This means less fixing and longer use.
- Household Appliances: Makers use slit coils for sinks, refrigerators, washing machines, and small tools.
- Industrial Manufacturing: You can use slit coils for stamping, making electrical cabinets, metal furniture, and pipes for water, gas, or oil.
Note: If you pick the right slitting line, your business can help many industries and meet high quality rules.
Choosing a Galvanized Coil Slitting Line
Coil Size and Material
When you pick a galvanized coil slitting line, you need to match it to your coil’s size and material. The thickness, width, and weight of each coil matter. These things decide what kind of slitting line you need. Heavy gauge lines can cut coils up to 20 mm thick and 35 tons. Thin gauge lines work with coils as thin as 0.2 mm and lighter weights.
|
Model |
Thickness Range (mm) |
Coil Width Range (mm) |
Coil Weight Range (tons) |
Line Speed (m/min) |
|
BELI-8*2000 |
8 – 10 |
600 – 2000 |
15 – 25 |
0 – 80 |
|
BELI-15*2600 |
15 – 20 |
600 – 2600 |
25 – 35 |
0 – 30 |
You also need to think about what the coil is made of. Harder metals, like high-carbon steel, make blades wear out faster. But they give cleaner cuts. The way the coil was made and its structure can change how the edges look. It also affects how long your tools last. Always check if the machine can work with different metals, like stainless steel or aluminum. Make sure it can change for different thicknesses too.
Production Needs
Pick a slitting line that fits your work goals. Think about how much you cut each day and what kinds of jobs you do. Some lines cut faster and can handle bigger coils. Others are better for small, careful jobs.

Choose machines that are strong and work well. Make sure they can handle your coil sizes and weights. Doing regular checks and careful handling helps stop problems. You should also look at prices and ask for quotes from different sellers. Some sellers give deals for big orders or long contracts. If you work in a busy place, like Los Angeles County, pick a seller with a service center close by. This saves on shipping and gets you help faster.
Automation Features
New slitting lines use smart automation to help you work better. Sensors and AI systems check coating thickness, temperature, and find defects. These features mean less work for people and fewer mistakes.
- Automated lubrication keeps machines running well and stops rust.
- Real-time checks help you find problems early and fix them fast.
- Cameras and sensors look for coating problems, so your quality stays the same.
- Automation makes the line faster and lets you finish more work. This saves time and money.
Tip: Automation helps you make better products, lowers labor costs, and keeps your work going smoothly.
Safety and Maintenance
You must keep your slitting line safe and in good shape. Regular checks and cleaning help you find problems and stop breakdowns. Always oil moving parts and check tension sensors for good cuts.
- Check and clean the uncoiler, slitter, and recoiler often.
- Sharpen or change slitter knives to keep cuts neat.
- Check if the machine is lined up right for smooth work.
- Take care of electrical and hydraulic parts.
- Wear safety gear and follow lockout/tagout rules when fixing things.
- Make a maintenance plan to find problems early.
- Adjust leveling rollers and guiding tables for each job.
- Clean pinching tools to stop slipping.
- Check the area at the end of each shift for dangers.
Note: Good safety and maintenance keep your workers safe and your slitting line working well.

Slitting line
Benefits
Efficiency
A galvanized coil slitting line helps you work faster. Automated systems let you finish more coils in less time. You do not need as many workers. One person can watch the whole line. This can lower labor costs by 20-30% in the first year. You can move workers to better jobs, like checking quality. Automated lines keep machines running longer and stop long breaks. You will see jobs like coil wrapping take half the time. These changes help you finish more work every day.
- Automated lines help you make up to 30% more than manual work.
- You need less space because automated systems are smaller.
- Robots do heavy or dangerous jobs, so work is safer.
Product Quality
A galvanized coil slitting line gives you good, steady results. Automation makes sure each strip is the right size and looks good. The system uses sensors to find problems early. You waste less metal and damage fewer coils. Machines handle the metal gently and carefully. Good packaging keeps your product safe when you ship or store it. Customers will see your products are better and more reliable.
- Automated lines lower damage and waste.
- You get better numbers for coil weight, size, and time.
- Good records help you track stock and improve your supply chain.
Flexibility
A modern slitting line lets you change orders fast. You can switch blade settings and coil sizes with little waiting. You can use many metals, like galvanized steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Automation makes it easy to change thickness and width. This helps you work for more industries and meet special requests from customers.
Tip: Flexible slitting lines help you keep up when customer needs change.
Innovations and Trends
Automation
Modern galvanized coil slitting lines use more automation now. Makers add PLC control systems to make machines smarter and quicker. These systems let you control each step, from uncoiling to recoiling. You can set up jobs by tapping a screen. Automation helps stop mistakes and keeps the line working well. Some new lines have robots that load coils and change blades. This means you do not have to lift heavy things as much. You can spend more time checking the quality of your work.
Tip: Automated lines help you finish jobs faster and keep workers safe.
Many companies buy energy-saving lines to use less power. These lines help you save money on bills. Some factories use advanced automation to waste less and work faster. With these new systems, you can do more jobs and send products out on time.
Measurement Systems
Today’s slitting lines use special measurement systems. Sensors check the coating thickness and surface quality as you work. These sensors help you find problems early. If you see a defect, you can fix it before it causes waste.
- Modern lines use cameras and lasers to measure strip width and thickness.
- You get alerts if the coating is too thin or thick.
- Data from these systems helps you meet strict quality rules.
Note: Good measurement systems help you make strong products for cars, appliances, and buildings.
Safety Upgrades
Safety upgrades help protect you and your team at work. New slitting lines have better guards, emergency stops, and sensors. These features stop the machine if something is wrong. Workers also get more training on how to use machines safely.
- Machines now have lockout/tagout systems to stop accidents during repairs.
- Sensors can tell if a hand or tool is too close to moving parts.
- Some lines use covers to keep dust and fumes away from workers.
Many companies use low-emission systems and zinc slag recovery now. These upgrades help you work in a cleaner and safer place. As more factories care about safety and the environment, you get better tools to protect your team and the earth.
Now you know how a galvanized coil slitting line works. It turns big steel coils into exact strips for many uses. This machine helps you work faster and make better products. It also lets you change what you make more easily. Before you buy one, think about what your factory needs. You should talk to experts or sellers for advice. You can visit a factory or look up different machines. This helps you find the best one for your business.
Tip: Trying the machine yourself helps you choose the right one.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a galvanized coil slitting line?
A galvanized coil slitting line cuts big steel coils into smaller strips. These strips are the right size for your work. Cutting coils this way saves time and cuts down on waste.
How do you maintain a slitting line for best performance?
You need to clean and check the machine often. Make sure to sharpen or change the knives when they get dull. Oil the moving parts so they work well. Always check the tension before you start a job. Taking care of the machine keeps it safe and working well.
Can you use a slitting line for different metals?
Yes, you can use the machine for many metals. It works with galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. Always check the settings and blades before you change the metal.
What safety steps should you follow when operating a slitting line?
Wear your safety gear every time you use the machine. Keep your hands away from the moving parts. Follow lockout/tagout rules when fixing the machine. Use guards and emergency stops to stay safe. Make sure everyone knows how to use the machine safely.
How does automation improve the slitting process?
Automation helps you control how fast and tight the machine works. It also sets the blades in the right place. This means you make fewer mistakes and get better strips. Automated machines need fewer workers and help keep everyone safe.

